

Innovation
At ARMMAN, we are building a continuous innovation process that is human-centred, data-driven, and evidence-based. We put the women we serve–pregnant women, mothers of infants, and health workers–at the centre of our innovation approach.
Our innovation process is iterative and cost-effective, and lets us design for scale using empathy and evidence. We actively leverage artificial intelligence to make our programmes more engaging and effective.

Human-centred innovation
We make sure that the voice of our users shapes the design and development of our products at every step of the innovation process

AI-POWERED SOLUTIONS
We partner with academic and research collaborators to make the best use of AI to make our programmes more engaging and effective

Data-driven approach
We use insights from how millions of users interact with our programmes and pilots to identify opportunities for innovation
Innovation sandboxes
We are creating sandboxes that cover the urban, rural and tribal contexts to act as controlled environments for testing our innovations across the country
Enhancing Impact through Innovation

HIGH-RISK PREGNANCY WHATSAPP PILOT FOR MaMitra
Know More >

HIGH-RISK PREGNANCY WHATSAPP PILOT FOR MaMitra
Know More >

Using WhatsApp
as a delivery
channel for
Kilkari 2.0
Know More >

Using WhatsApp as a delivery channel for Kilkari 2.0
Know More >

WhatsApp
chatbot for
health
workers
Know More >

WhatsApp chatbot for health workers
Know More >

High Risk
pregnancy
pilot for
Kilkari
Know More >

High Risk pregnancy pilot for Kilkari
Know More >

Prediction
model using
Artificial
Intelligence
Know More >

Prediction model using Artificial Intelligence
Know More >
A pilot was conducted in Vasai-Virar, on the outskirts of Mumbai, to support pregnant women identified with the high risk condition of moderate to severe anaemia.
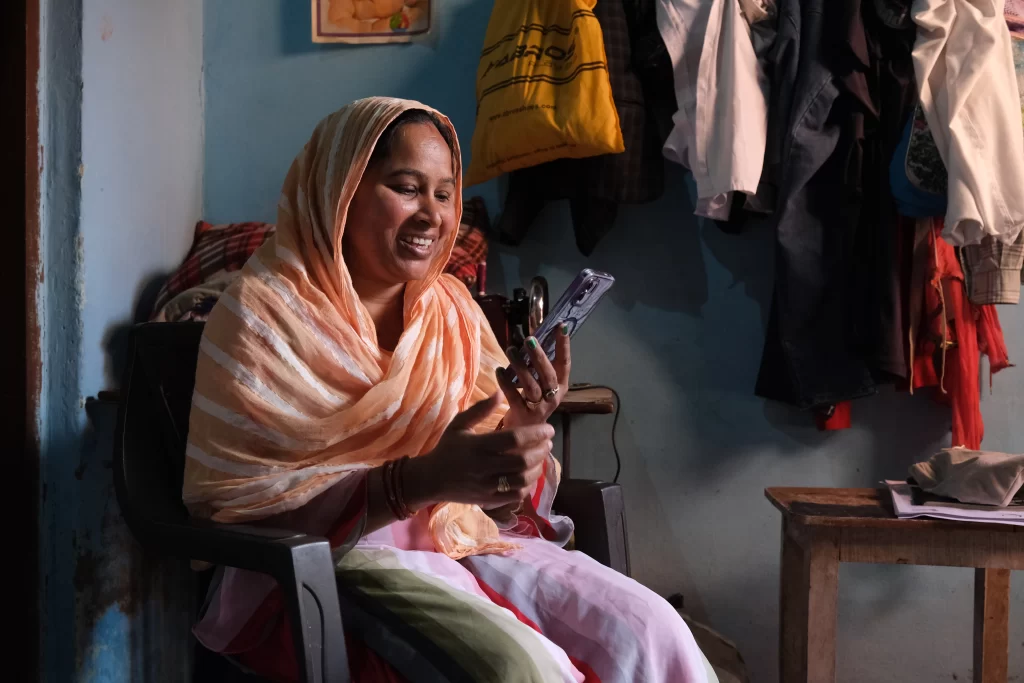
Participants received weekly WhatsApp video messages focused on Iron and Folic Acid (IFA) adherence, nutrition, danger signs, and other key topics, along with interactive nudges to encourage positive behavior change.
To support continuity of care, community health workers were trained to visit participants every 30 days, measure haemoglobin levels of the participants, and deliver counseling.
Building on the success of this pilot, the programme has now been scaled in partnership with the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC) under the MaMitra initiative to 11 BMC Hospitals.
It now includes five additional high-risk conditions, hypertension, diabetes, hypothyroidism, poor obstetric history, previous LSCS, and delivers tailored messages to help women better manage their high-risk pregnancies.
60%
women reported watching all
or most videos
79%
of women showed an increase
in haemoglobin levels
6%
had complete anemia reversal
The upcoming Kilkari 2.0 will leverage multiple delivery channels, including voice calls, WhatsApp, YouTube, to deliver targeted messages with richer multimedia content.
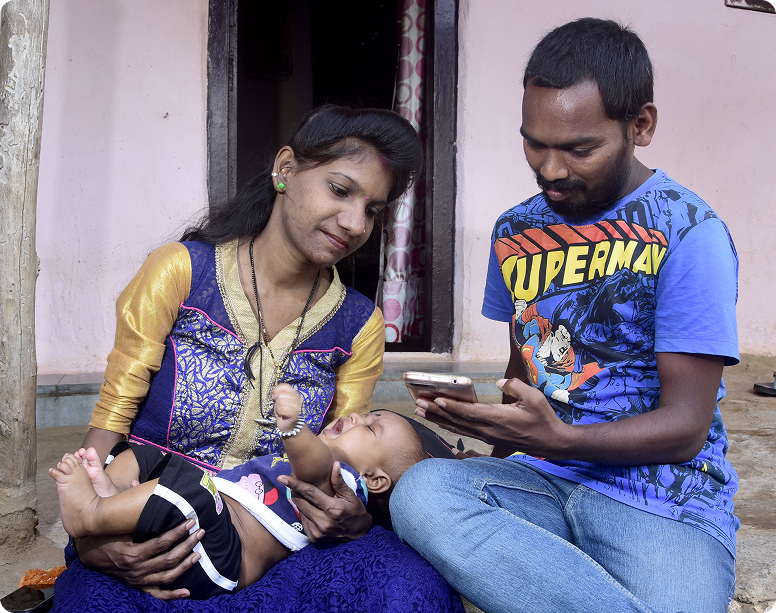

Women and children at low risk will receive nuanced voice calls and multimedia content, along with two-way communication through WhatsApp, depending on their access to smartphones.
Those with high-risk conditions and/or facing equity related challenges will receive targeted content,
two-way communication, and long-term support via call centre and WhatsApp.
The pilot to test the feasibility and effectiveness of WhatsApp as a delivery channel for Kilkari was conducted from May to October 2023 among 480 Women in Jharkhand and Haryana.
These insights are helping shape the development of Kilkari 2.0. The innovation will be scaled up to 2-3 states in 2024-25 and pan India from 2025-26.
The results from the pilot emphasise the effectiveness of videos, the reinforcing role of posters, and the importance of incorporating state-specific dialects in content.
ARMMAN has developed a multilingual, multimodal AI-powered chatbot in collaboration with ARTPARK, with support from the Gates Foundation and Google.org Generative AI Accelerator. This WhatsApp-based ANM Support System enables continuous learning along with on-the-job support for the Auxiliary Nurse Midwives (ANMs), trained to manage, track and refer high risk pregnancies through the Integrated High Risk Pregnancy Tracking and Management (IHRPTM) Programme.
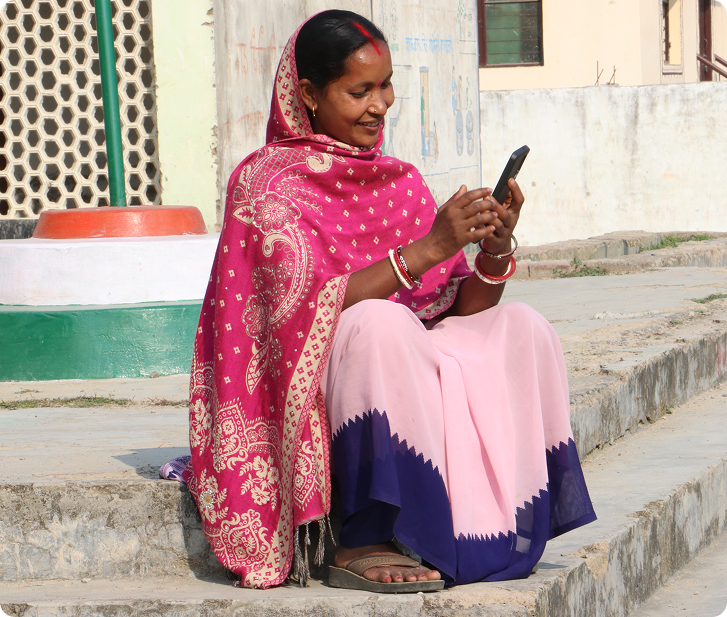

The chatbot is currently live in three districts of Uttar Pradesh – Shravasti, Sambhal, and Kaushambi – where over 750 ANMs are accessing real-time, clinically validated guidance on managing high-risk pregnancies.
Available in Hindi, English, and Hinglish via WhatsApp, the co-pilot delivers personalized support, empowering frontline workers to deliver timely, informed care and improving maternal and child health outcomes.
87%
ANMs return for a second session
97%
positive user feedback
91%
responses rated as completely satisfactory by a medical expert
A pilot was conducted in Ganjam and Sundargarh districts of Odisha for pregnant women who are Kilkari subscribers suffering from diabetes, hypertension and severe anemia. As part of the pilot, recorded voice calls with targeted content on these conditions were sent directly to the mobile phones of the women for 10 weeks.
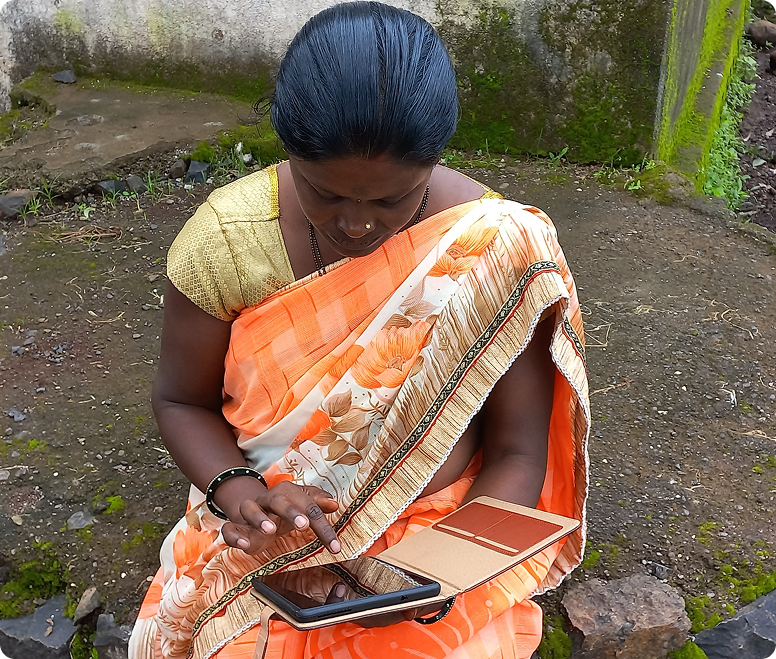

The calls addressed topics such as :
- symptoms of the high risk conditions,
- danger signs,
- need for regular check-ups,
- nutrition related information,
- care during delivery,
- postpartum care, and
- adoption of healthier practices for long-term outcomes.
women have
completed the pilot.
A telephonic survey conducted with the first group of women who received the calls, informed that
health practices to manage their
high risk condition
to consuming more
nutritious meals
On completion of the pilot, a large scale research evaluation will be conducted and then we aim to integrate
the content into Kilkari 2.0.
ARMMAN partnered with Google Research and IIT Madras to design Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based predictive models to identify women who were at risk of dropping out from our flagship programme, mMitra.
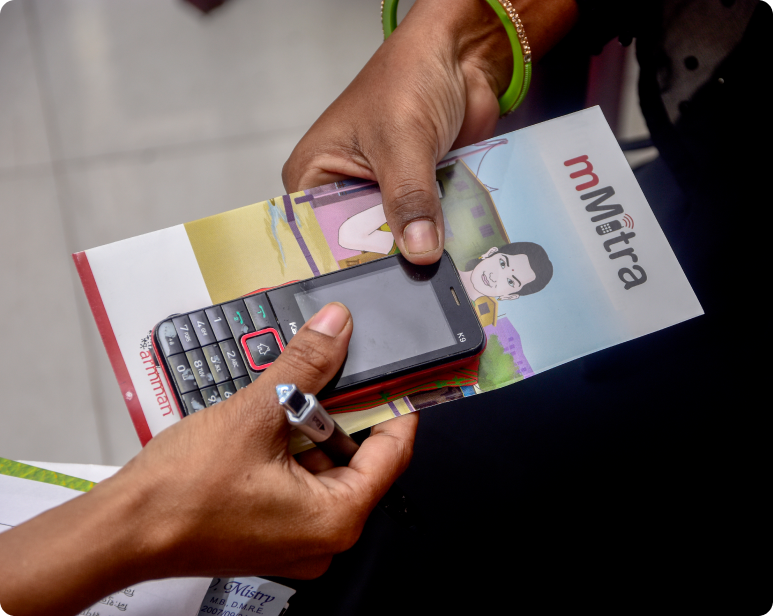

mMitra is ARMMAN’s free mobile-based voice call service that sends timed and targeted critical preventive care information directly to the phones of the enrolled women through pregnancy and infancy.
The prediction model is built on analysis of anonymised call records of women registered in mMitra.
call records
in mMitra
With support from Google Research and leveraging past call history data from mMitra, learning based models (Convolutional Neural Disengagement Predictor and Recurrent Neural Disengagement Predictor) were built to predict and identify participants most at risk of disengaging and dropping out from the mMitra programme.
These predictions helped us identify women requiring more involvement and interventions from health workers and counsellors. An easy-to-use dashboard for health workers was also developed to visualise predicted risk of drop-off.
A pilot was conducted in Ganjam and Sundargarh districts of Odisha for pregnant women who are Kilkari
subscribers suffering from diabetes, hypertension and severe anemia. As part of the pilot, recorded voice calls
with targeted content on these conditions were sent directly to the mobile phones of the women for 10 weeks.
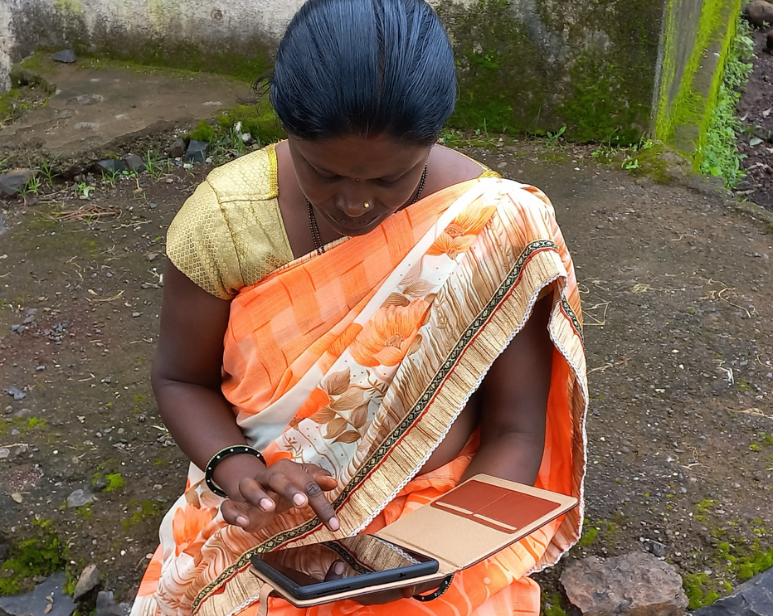

The calls addressed topics such as :
- symptoms of the high risk
- conditions,
- danger signs,
- need for regular check-ups,
- nutrition related information,
- care during delivery,
- postpartum care, and
- adoption of healthier practices for long-term outcomes.
women have
completed the pilot.
A telephonic survey conducted with the first group of women who received the calls, informed that
On completion of the pilot, a large scale research evaluation will be conducted and then we aim to integrate
the content into Kilkari 2.0.
The upcoming Kilkari 2.0 will leverage multiple delivery channels, including voice calls, WhatsApp, YouTube,
to deliver targeted messages with richer multimedia content.
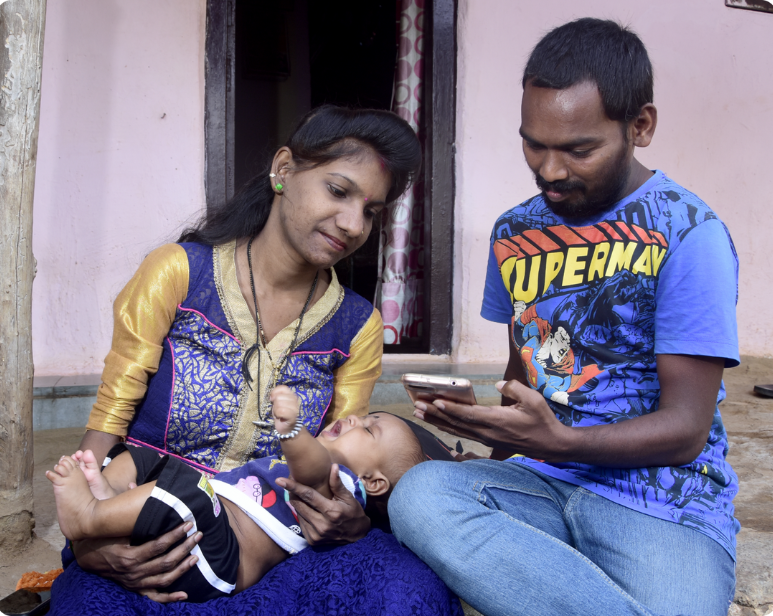

Women and children at low risk will receive
nuanced voice calls and multimedia content, along
with two-way communication through WhatsApp,
depending on their access to smartphones.
Those with high-risk conditions andor facing equity
related challenges will receive targeted content,
two-way communication, and long-term support
via call centre and WhatsApp.
The pilot to test the feasibility and effectiveness of whatsApp as a delivery channel for Kilkari was conducted from May to October 2023 among
and Haryana.
These insights are helping shape the development
of Kilkari 2.0. The innovation will be scaled up to
The results from the pilot emphasise the effectiveness of videos, the reinforcing role of posters, and the importance of incorporating state-specific dialects in content.
Recently we won the Grand Challenges Grant for Catalysing Equitable Artificial Intelligence (AI), an initiative aimed at catalysing innovation to address urgent global health and development issues, funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF).
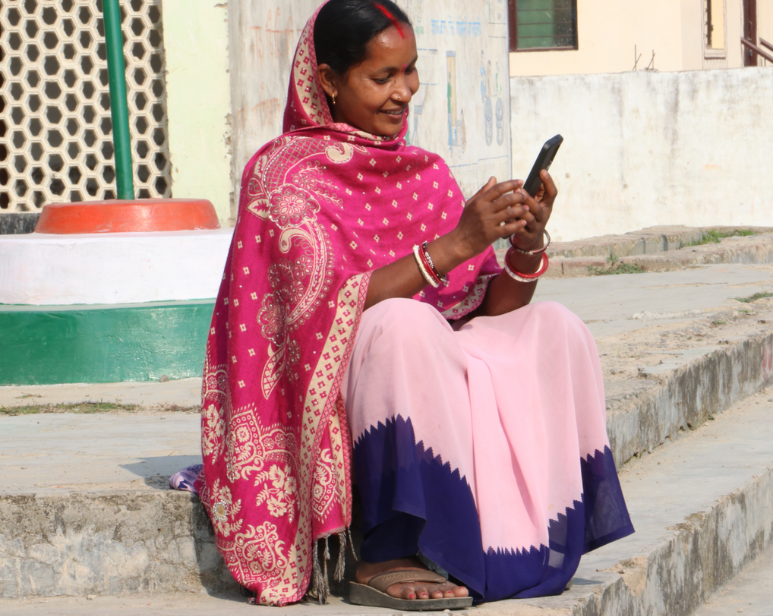

This grant is helping us to integrate Large
Language Models (LLM) – powered co-pilot into
the existing learning and support application to
improve the training of Auxiliary Nurses and
Midwives (ANMs) so they can better manage
high-risk pregnancies.
We have developed a multilingual and
multimodal chatbot that responds to ANMs’ text
and voice queries on high-risk pregnancies and
antenatal care in English and Telugu.
Earlier, a Medical Officer would answer the doubts and queries of the ANMs through the learning and support application. The model has demonstrated an accuracy of over
on shown for the support tool
with user testing with ANMs
showcasing its precision in
across addressing ANMs’ queries.
HIGH-RISK PREGNANCY WHATSAPP PILOT FOR MaMitra
A pilot was conducted in Vasai-Virar, on the outskirts of Mumbai, to support pregnant women identified with the high risk condition of moderate to severe anaemia.

Participants received weekly WhatsApp video messages focused on Iron and Folic Acid (IFA) adherence, nutrition, danger signs, and other key topics, along with interactive nudges to encourage positive behavior change.
To support continuity of care, community health workers were trained to visit participants every 30 days, measure haemoglobin levels of the participants, and deliver counseling.
Building on the success of this pilot, the programme has now been scaled in partnership with the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC) under the MaMitra initiative to 11 BMC Hospitals.
It now includes five additional high-risk conditions, hypertension, diabetes, hypothyroidism, poor obstetric history, previous LSCS, and delivers tailored messages to help women better manage their high-risk pregnancies.
60% women reported watching all or most videos
79% of women showed an increase in haemoglobin levels
6% had complete anemia reversal
Using WhatsApp as a delivery
channel for Kilkari 2.0
channel for Kilkari 2.0
The upcoming Kilkari 2.0 will leverage multiple delivery channels, including voice calls, WhatsApp, YouTube, to deliver targeted messages with richer multimedia content.

Women and children at low risk will receive nuanced voice calls and multimedia content, along with two-way communication through WhatsApp, depending on their access to smartphones.
Those with high-risk conditions and/or facing equity related challenges will receive targeted content,
two-way communication, and long-term support via call centre and WhatsApp.
The pilot to test the feasibility and effectiveness of WhatsApp as a delivery channel for Kilkari was conducted from May to October 2023 among 480 Women in Jharkhand and Haryana.
These insights are helping shape the development of Kilkari 2.0. The innovation will be scaled up to 2-3 states in 2024-25 and pan India from 2025-26.
The results from the pilot emphasise the effectiveness of videos, the reinforcing role of posters, and the importance of incorporating state-specific dialects in content.
WhatsApp chatbot for health workers
Recently we won the Grand Challenges Grant for Catalysing Equitable Artificial Intelligence (AI), an initiative aimed at catalysing innovation to address urgent global health and development issues, funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF).

This grant is helping us to integrate Large Language Models (LLM) – powered co-pilot into the existing learning and support application to improve the training of Auxiliary Nurses and Midwives (ANMs) so they can better manage high-risk pregnancies.
We have developed a multilingual and multimodal chatbot that responds to ANMs’ text and voice queries on high-risk pregnancies and antenatal care in English and Telugu.
Earlier, a Medical Officer would answer the doubts and queries of the ANMs through the learning and support application. The model has demonstrated an accuracy of over
93%
70%
High Risk pregnancy pilot for Kilkari
A pilot was conducted in Ganjam and Sundargarh districts of Odisha for pregnant women who are Kilkari subscribers suffering from diabetes, hypertension and severe anemia. As part of the pilot, recorded voice calls with targeted content on these conditions were sent directly to the mobile phones of the women for 10 weeks.

The calls addressed topics such as :
- symptoms of the high risk conditions,
- danger signs,
- need for regular check-ups,
- nutrition related information,
- care during delivery,
- postpartum care, and
- adoption of healthier practices for long-term outcomes.
women have
completed the pilot.
A telephonic survey conducted with the first group of women who received the calls, informed that
women made changes in their health practices to manage their high risk condition
to consuming more
nutritious meals
Prediction model using
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence
ARMMAN partnered with Google Research and IIT Madras to design AI-based predictive modeling technology that provided an indication of women who were at risk of dropping out from our flagship programme, mMitra.

mMitra is ARMMAN’s free mobile-based voice call service that sends timed and targeted critical preventive care information directly to the phones of the enrolled women through pregnancy and infancy.
The prediction model is built on analysis of anonymised call records of women registered in mMitra.
call records
With support from Google Research and leveraging past call history data from mMitra, learning based models (Convolutional Neural Disengagement Predictor and Recurrent Neural Disengagement Predictor) were built to predict and identify participants most at risk of disengaging and dropping out from the mMitra programme.
These predictions helped us identify women requiring more involvement and interventions from health workers and counsellors. An easy-to-use dashboard for health workers was also developed to visualise predicted risk of drop-off.
